2025 SpyCloud Identity Exposure Report
Unraveling New Dimensions
of Identity Threats
Defenders must be able to rapidly correlate exposed user identity data –
past and present, work and personal
– to proactively and comprehensively prevent targeted cyberattacks.
DIGITAL IDENTITY WARS
the struggle for power in cyberspace
In 2024, digital identities became the top target for cybercriminals, serving as the convergence point for personal, professional, and organizational risk. Ninety-one percent of organizations reported suffering an identity-related incident in the past year – nearly double the previous year’s reported numbers – and nearly 80% of breaches still involve the use of stolen credentials.
A new truth is abundantly clear: Attackers are taking advantage of the vast user footprints scattered across the dark web – spanning usernames, passwords, personally identifiable information (PII), device details, session cookies, and more – to wage an identity war that’s quickly escalating.
Without a comprehensive defense strategy, organizations risk falling behind in an arms race where cybercriminals are continuously refining their tools and tactics, leveraging stolen data from breaches, infostealer malware, phishing campaigns, and high-precision combolists to automate and scale attacks with unprecedented efficiency.
This report details the astronomical scale of the risks posed by digital identity sprawl, summarizes the top threats to organizations, and provides guidance on how to shift our collective defenses to magnify success.
THE MISSION:
GO BEYOND
THE TRADITIONAL IDENTITY FRONTIER
“[The identity threat landscape] is big. You just won’t believe how vastly, hugely, mind-bogglingly big it is.”
Our mission at SpyCloud is to disrupt cybercrime by stopping bad actors’ ability to profit off of stolen data. To do that we have to operate in the same plane, decoding the ever-growing, complex web of stolen data in their’ hands – be it from traditional data breaches or stealthy infostealer malware, timely combolists or sophisticated phishing campaigns.
The Identity Threat Landscape, By the Numbers
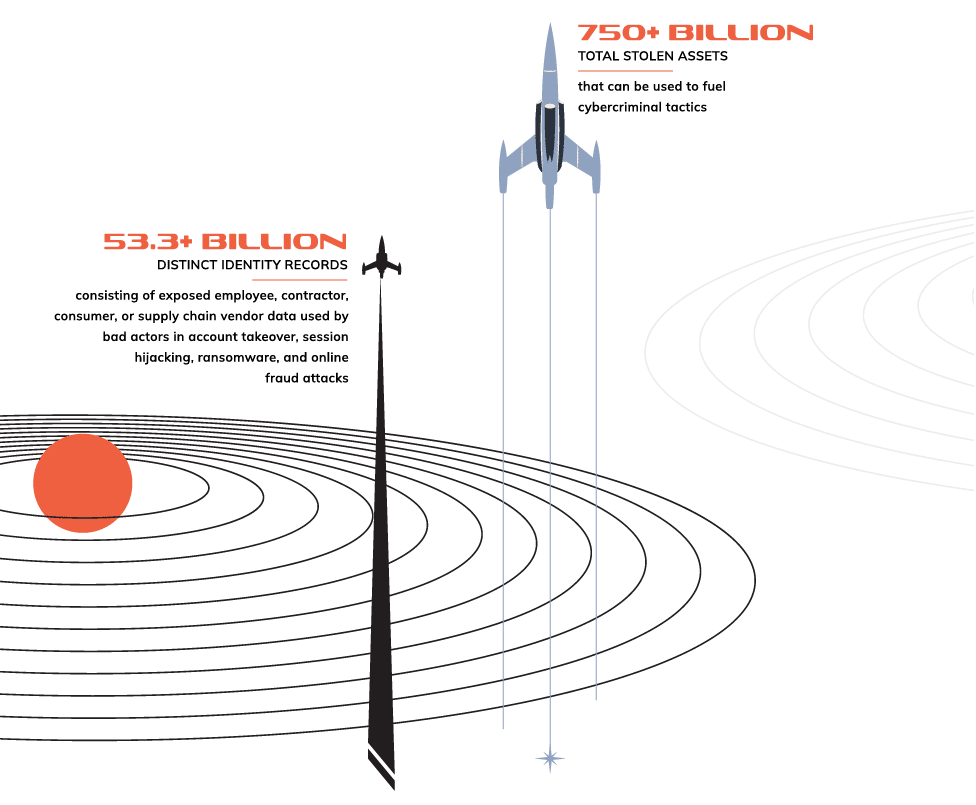
SpyCloud’s total collection of recaptured data grew 22% in the past year, from 43.7 billion to 53.3 billion distinct identity records, highlighting the vast scale of stolen data available to attackers – and the undeniable demand for a proactive, identity-centric approach to tackling darknet exposures.
Important for understanding the data in this report
An asset is a single data point associated with a digital identity. For example, an email address or password.
A record is a collection of data points associated with a given digital identity, exposed via a single breach, malware infection, combolist, or phishing campaign. For example, a record could include an email address, password, IP address, and device details for a user.
Exposed identity data is what criminals use to fuel targeted cyberattacks, and there is a lot of it circulating in the criminal underground. SpyCloud has recaptured:
Despite the growing prevalence of identity-based cybercrime, many organizations and consumers remain insufficiently aware of the massive breadth of digital identity data stolen from users and traded on the darknet. Through deep analysis of the criminal underground, we can illuminate hidden dangers and provide the knowledge security teams need to protect their users.
Venture out with us as we explore the previously unknown.
HOUSTON...
WE HAVE AN
IDENTITY THREAT PROBLEM
“The [holistic identity] is not only [more vast] than we imagine, it is [more vast] than we can imagine.”
Shifting to a Holistic Model to Map Identity Exposure
Historically, account-centric security focused on single data points – like compromised email addresses or passwords – but this approach fails to capture the full complexity of modern threats. SpyCloud has pioneered the holistic identity-centric model, aggregating breach, malware, combolist, and phishing exposures tied to a single individual across their many online personas – ensuring defenders understand the broad scale of identity exposures that may make their business a target. This shift is critical in identifying true risks before they escalate into full-scale attacks.
When we take a holistic approach and connect fragmented identity exposures across multiple sources and over time, the true scale of exposure becomes far more alarming. By broadening the perspective, SpyCloud researchers reveal a much deeper and more pervasive risk.
How Do We Define Identity Exposures Today?
Traditional exposure
This is the traditional understanding of identity exposure – piecemeal compromised data associated with a user that illuminates some of a person’s darknet exposures, but not comprehensively nor in correlation with other exposures.
Holistic exposure
Cybercriminals have massive amounts of identity data from multiple sources at their disposal – including data breaches, infostealer malware infections, phishing campaigns, and combolists – which makes attacks easier, more targeted, and more effective. A holistic identity approach is a necessary evolution for understanding and remediate the full scope of user exposures that affect the organizations with which they work and do business.
By expanding exposure analysis beyond a single data point, defenders can uncover a more complete picture of identity exposure – one that highlights the robust amount of stolen data criminals can leverage in follow-on attacks.
Charting the Scale of Identity Exposure
A single identity asset can become the first spark in a sprawling cyber constellation when exposed. But when you zoom out with a holistic lens, it becomes evident that identity exposure isn’t isolated – it’s part of a vast, interconnected digital constellation that cybercriminals use to chart and abuse their victims’ online footprint.

records per consumer
frequently including exposed PII like full names, dates of birth, and phone numbers, as well as Social Security/ID numbers, addresses, and credit card or bank information.
74% of recaptured consumer records contain a physical or IP address
unique
usernames
unique
emails
credential
pairs
total
usernames
total
emails
unique
sources
The Trajectory of
Stolen Data
from Source to Threat
“Exploration is wired into our brains. If we can see the horizon, we want to know what’s beyond.”
SpyCloud tracks the threats to digital identities that evolve from multiple sources, each contributing to the cosmic scale of modern identity exposure:
Infostealers silently infiltrates devices, extracting sensitive data such as login credentials, PII, browser cookies, and system details. This stolen information forms the foundation for account takeover, fraud, ransomware, and other cybercrimes.
Phishing attacks have transformed into industrial-scale operations, leveraging phishing-as-a-service platforms. These tools automate the creation of sophisticated phishing kits, enabling cybercriminals to harvest credentials, 2FA codes, and browser session cookies with alarming efficiency.
Data breaches, ranging from widely publicized incidents to lesser-known leaks, continuously contribute to the pool of exposed identities. These breaches often serve as the initial entry point for subsequent attacks, amplifying their impact across industries and geographies.
2024 saw the return of the combolist, blurring the lines between traditional breaches and active malware exploitation. Combolists – often dismissed as unreliable in the past – are making a comeback, now more likely to be curated from fresh infostealer logs, achieving match rates of up to 98% with authentic credentials.
The Infostealer Malware Problem
Infostealer malware stands out as a particularly insidious force in the world of identity threats, silently exfiltrating credentials and personal data at mind-boggling scale. Ninety-five percent of identity teams are “extremely or significantly concerned” about data siphoned from malware-infected devices being used for more harmful attacks, and rightfully so.

Understanding infostealers’ role in identity exposure is crucial to mitigating the growing risks organizations and individuals face.
In 2024, criminal use of infostealer malware at least doubled, reaching unprecedented levels and posing heightened risk to organizations and individuals alike. SpyCloud’s analysis of malware-related breaches provides a clear picture of the scale and severity of this persistent threat.
In 2024, SpyCloud recaptured:
unique malware infection logs
(email addresses, usernames, and passwords plus login domains), revealing the vast scale of data harvesting.
An average of 44 exposed credentials per infection, showcasing the depth of data extracted from individual infections.
emphasizing the scale of session hijacking opportunities for cybercriminals
An average of 1,861 cookies were harvested per infection, showcasing the depth of information extracted from a given device.
Cybercriminals also use infostealers to infiltrate third-party business applications, which through our research shows that, on average, could expose access to 10 to 25 business applications from just a single infection. Add to that the fact that the average organization has more than 300 applications – technically, a single malware infection can expose access to all of them.
In 2024, we also observed attackers targeting enterprise AI tools that could contain proprietary insights, intellectual property, and sensitive business data, as well as password managers to gain footholds and exploit access to corporate data wherever possible.
stolen credential records for third-party applications
a 48% increase from the year prior – harvested from managed and unmanaged devices, including many popular business tools.
stolen credential records for enterprise AI tools
stolen credential records from popular password managers
threatening critical security tools.
Key Malware Families and Trends
Infostealers remain pivotal to malware operations. SpyCloud kept tabs on nearly 75 different malware families in 2024, some of the most troublesome including:
This infostealer has rapidly evolved, incorporating advanced evasion techniques and increasing its threat potential. Recent updates include improvements in data theft capabilities, allowing it to bypass Google’s App-Bound Encryption for stealing cookies and credentials. It now exfiltrates stolen data in real-time, ensuring partial logs reach attackers even if execution is interrupted. Additionally, LummaC2 has integrated GhostSocks, turning infected devices into residential proxies that enable threat actors to bypass security measures and monetize access. These enhancements make LummaC2 a persistent and adaptable threat that continues to challenge defenders.
SATURATION OF LummaC2 INFFECTIONS IN THE STEALER LANDSCAPE IN 2024
In 2024, law enforcement’s Operation Magnus successfully reduced the proliferation of Redline Stealer and Meta Stealer logs. As Redline infections declined, we saw LummaC2 surpass it in the latter half of the year, claiming more market share and replacing Redline’s previous position as the most prominent stealer.
Open Source Stealers
It was particularly interesting to note a rise of open source stealers in 2024. The criminals using these stealers don’t have to pay for a malware-as-a-service (MaaS offering), but are often still successful in harvesting stolen data. We observed a growing number of open source stealers last year, including:
AsyncRAT
A remote access tool with stealer capabilities, often exploited for keystroke logging, remote desktop control, and malware deployment. SpyCloud observed a notable uptick in stealer logs from successful AsyncRAT infections.
Blank Grabber
A Python-based stealer that captures system information and running processes in multiple languages, using native Windows commands for stealth.
Vega Stealer
A newly emerging Python-based stealer, different from the legacy .NET Vega Stealer from 2018. SpyCloud is monitoring its activity, though no stolen data has surfaced yet.
Phemedrone
A C#-based stealer featuring credential and cookie tagging, with a special focus on Russian targets.
macOS Stealers
We keep close tabs on macOS stealers because there is a historical misconception that malware doesn’t target Macs. As Apple devices steadily capture more market share with individuals and within corporate environments, macOS malware becomes more worthwhile for criminals to create and deploy. Some examples we observed in 2024 include:
Atomic macOS Stealer
A widely distributed stealer-as-a-service malware that extracts credentials, browser data, cryptocurrency wallets, and system information from macOS devices.
Banshee Stealer
Unidentified Eos Stealer
A yet-unnamed macOS stealer capable of extracting credentials from Apple’s Keychain, similar in nature to Banshee and Atomic macOS Stealers.
How Malware Fuels Cybercrime
Infostealer malware enables data exfiltration by extracting login credentials, session cookies, auto-fill data, device information, and much more – its capabilities extending well beyond simple credential theft.
- Malware fuels targeted account takeover (ATO) attacks, where specific stolen data is sought out by criminals to take over accounts of high-value individuals or at specific organizations.
- Cookies siphoned by infostealers enable session hijacking, allowing criminals to sidestep MFA and even passkeys to take over active web sessions.
- Infostealer malware is the first domino in a ransomware attack, arming criminals with credentials and cookies to access enterprise networks and encrypt data.
- Malware-exfiltrated data gives criminals personal and financial information needed to conduct identity theft and financial fraud.
- Malware also powers botnets for credential stuffing and phishing attacks, amplifying cybercriminal operations at scale.
The Phishing Machine
Key PhaaS Platforms and Trends
Phishing campaigns are increasingly focusing on high-value data, with attackers targeting corporate credentials to enable lateral movement within organizations, financial accounts to access bank logins and cryptocurrency wallets, and stolen session cookies to bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Within the millions of records SpyCloud recaptured in 2024 are emails (97% of records we collected contain at least one email address) and location data, mostly in the form of IP addresses (64%), though about half of our recaptured phish data included specific city or postal code information.
Phished data often also includes browser-specific information such as user agents, which can contain information about the device – whether it’s mobile or desktop, and what operating system it’s using – as well as the browser itself.
Taken together, this data is incredibly valuable for adversaries and the consequences for organizations are clear – and severe.
Caffeine/ONNX
Caffeine was a PhaaS platform that was first active in 2022, offering a user-friendly dashboard and a full suite of tools to conduct phishing campaigns, including more advanced features like dynamically generated pages with pre-populated victim information. Caffeine also offered an open registration process, allowing anyone to set up an account themselves without having to reach out to an admin. This made it extremely easy to procure, set up, and use.
Fast forward and PhaaS platforms like ONNX (a revised and rebranded version of Caffeine) further industrialized phishing in 2024, providing attackers with turnkey kits that capture 2FA codes in real time, deliver phishing links via QR codes, and evade Cloudflare CAPTCHA to bypass detection. SpyCloud recaptured over 1.7 million phished records between ONNX and Caffeine in the second half of 2024, although the ONNX store went dark towards the end of the year, potentially as a result of researchers revealing the identity of its operator, MRxC0DER, as Abanoub Nady.
The Data Breach Impact
Much like in previous years, there were a series of significant data breaches in 2024 that underscored ongoing vulnerabilities in digital systems worldwide – the magnitude of which was highlighted by the Mother of All Breaches (MOAB) and National Public Data Breach. According to reported numbers, 2024 saw the second-highest number of data breaches on record.
In 2024, SpyCloud recaptured:
breach records
breaches with more than 50 million stolen records
From corporate databases to governmental entities, these breaches highlight the wide-ranging implications of exposed data.
Mother of All Breaches (MOAB)
Discovered in January 2024, the Mother of All Breaches (MOAB) is one of the largest aggregated data leaks ever recorded, exposing 26 billion records compiled from over 4,000 breaches. The dataset includes email addresses, phone numbers, usernames, passwords, and other sensitive details from major domains like qq.com and zeeroq.com. While much of the data had alr eady been circulating in underground forums, the sheer volume and accessibility of MOAB highlight the ongoing risk s of large-scale data aggregation and poor database securit y. Researchers also found 1.6 billion previously unseen records, including a large-scale breach of QQ.com, reinforcing concerns about the silent spr ead of compromised credentials long before they are made public.
MOAB exemplifies how stolen data remains valuable long after an initial breach, fueling credential stuffing, account takeover, and identity fraud. The dataset’s accessibility lowers the barrier for cybercriminals to exploit exposed credentials, making proactive security measures, continuous monitoring, and strict access controls more critical than ever.
National Public Data (NPD) Breach
The National Public Data (NPD) breach, first appearing for sale in April 2024 and later leaked for free in August, exposed 2.7 billion records, including highly sensitive personally identifiable information (PII) such as full names, Social Security numbers (SSNs), addresses, birth dates, and phone numbers. Originally attributed to a background check company, the dataset contains 272 million unique SSNs (accounting for roughly 80% of the US population) and 420 million addresses – making it a goldmine for identity theft and financial fraud. Cybercriminals can leverage this data for new account fraud, phishing attacks, and synthetic identity creation, increasing the long-term risks for affected individuals.
With historical records and alternative identity details included, the breach makes bypassing identity verification measures easier than ever. Criminals can piece together full identity profiles, enabling them to open fraudulent accounts, steal tax refunds, and evade traditional fraud detection systems. The NPD breach serves as a stark reminder that once sensitive data is exposed, it becomes a permanent risk, potentially fueling cybercrime for years to come.
The Neverending
Orbit
of Stolen Data
“The thing about [stolen data] – the [criminal underground] – is that it’s infinite. No end and no beginning.”
About Our Recaptured Data
At the root of the crimes most costly to businesses – account takeover, ransomware, and fraud – are identity exposures that give attackers a way in. SpyCloud continuously ingests and analyzes more than 25 billion pieces of stolen identity data every month – the same data criminals are using to fuel targeted cyberattacks.
Our focus extends from exposed credentials to include stolen cookies, personally identifiable information (PII), financial information, and more tied to individuals across their many online personas.
Exposed Popular Passwords
Passwords remain both a cornerstone of identity security and a glaring weak spot. Despite ongoing education efforts, many users still rely on common, weak, or recycled credentials, fueling widespread security risks.
SpyCloud’s 2024 research reveals the staggering scale of exposed credentials circulating within the criminal underground:
(username/email + password)
billion
a 125% increase from 2023
of which SpyCloud cracked and delivered as plaintext passwords, making it possible to quickly verify if exposed credentials exactly match those in-use by employees and customers.
The Gravitational Pull of Common Passwords
The most commonly exposed passwords in 2024 remain dishearteningly familiar:
And To Make Things Worse
While predictable choices seem to persist due to poor cyber hygiene practices, password reuse also remains a pervasive problem, and the data from 2024 shows that unfortunately it’s not getting any better. An alarming 70% of users exposed in breaches last year reused previously-exposed passwords across multiple accounts.
All-Time Password Reuse Rate
Pop Culture’s Sphere of Influence on Trending Passwords
In 2024, millions of exposed passwords reflected a mix of pop culture references, seasonal themes, favorite animals, and sports events, making them both creative and predictable. These trends may feel personal and easy to remember for users, but their widespread popularity also makes them prime targets for attackers.
Top baseword trends for commonly exposed passwords:
Despite increasing awareness campaigns and security tools, users continue to fall into the trap of convenience over security. The adoption of stronger and unique passwords by users, and the adoption of NIST best practices and automated remediation by organizations is paramount to enterprise and identity security.
Trending Popular Password Tracking
SpyCloud tracks password exposure closely, paying attention to the trending topics of the world and where they may influence password use. We update a list of poor passwords that are being exploited by criminals on our website monthly so individuals can check if their passwords are circulating the dark web and, if so, change or ban them immediately. We also recommend organizations add these to their banned password lists for an added layer of protection.
PII Exposure
The exposure of personal information continues to escalate, posing severe risks to individuals and organizations worldwide. SpyCloud’s 2024 analysis reveals a troubling increase in the volume and variety of exposed PII, underscoring the urgency of safeguarding sensitive data.
The Spectrum of PII Exposure
SpyCloud recaptured 32.22 billion PII assets in 2023, and the numbers for 2024 highlight a staggering upward lift by 39% to 44.8 billion PII assets. This increase was largely driven by major breaches like the National Public Data (NPD) breach, which exposed an unprecedented volume of Social Security numbers and other PII due to its origins as a background check company.
From financial records to government-issued IDs, the breadth of compromised data underscores the scale of potential exploitation. High-value targets, such as Social Security and passport numbers, are particularly lucrative in the criminal underground, often selling for premium prices due to their ability to facilitate fraud. Meanwhile, the dramatic rise in exposed driver’s licenses and passports signals a shift in cybercriminal tactics, as they increasingly target comprehensive identity elements to fuel fraud and identity theft on a broader scale.
Pinpointing Where Data is Sold and Traded
Stolen Session Cookies
In the intricate web of cybercrime, stolen session cookies have become a powerful tool for attackers, allowing them to bypass authentication measures and hijack accounts. Session cookies are increasingly targeted by cybercriminals seeking to impersonate legitimate users without running into MFA or other security defenses.
How Attackers Steal Session Cookies
Cybercriminals harvest stolen cookies through various tactics, including:
Malware families such as RedLine and LummaC2 collect session cookies alongside credentials and autofill data, allowing attackers to bypass security protocols.
Modern phishing platforms now target session cookies in addition to login credentials, increasing their effectiveness in account takeovers.
SpyCloud’s 2024 findings highlight the widespread availability and exploitation of stolen session cookies:
enterprise applications
financial services
administrative platforms
Cybercriminals are increasingly refining their methods to maximize the effectiveness of stolen session cookies. Admin and privileged accounts have become top targets, as these sessions grant access to corporate systems and sensitive data. Attackers are also cross-referencing stolen session cookies with other identity data, building detailed user profiles for more targeted and effective account takeover attacks. With these evolving tactics, session cookie theft is a massive risk that should be on every defender’s radar.
Other Targeted Data Types
The emerging trends we observed in 2024 had a recurring theme: malicious actors are taking full advantage of the expanding digital identity. That trend extends to targeting other data types, ranging from financial information to API keys. SpyCloud’s 2024 findings highlight this shift:
API keys exposed
Cryptowallet addresses targeted
Credit cards stolen
Aligning Your
Course to the
Identity Horizon
Strategies for 2025
“…to boldly go where no security team has gone before”
In the vast expanse of the cyber world, defending user identities can increasingly feel like navigating an uncharted universe. With the right strategies and tools, organizations can shift the balance of power and turn the tide.
SpyCloud’s solutions, equipped with automated identity analytics and automated remediation, serve as a powerful shield against the relentless wave of threats. By recapturing, analyzing, and correlating stolen identity data, SpyCloud equips organizations with critical insights to safeguard identities and prevent attacks.
This report is intended to illuminate the data exposed on the dark web and the most urgent cybercrime trends that take advantage of stolen data so teams can fortify defenses and remediate potential risks. Cybercriminals are clearly leveraging breaches, phishing-as-a-service platforms, combolists, and infostealer malware to harvest mass quantities of identity data to launch their attacks.
Success in Fighting Cybercrime: 2024 Highlights
2024 wasn’t all doom and gloom. We saw significant victories in the battle against cybercrime that inspire us and showcase the power of collaboration, innovation, and persistence in disrupting criminal operations, including:
- Operation Magnus
- Operation Cronos
- The arrest of USDoD
- The crackdown on Telegram
Organizations must take proactive steps that center around an understanding of the holistic identity to build more robust threat protection now and into the future:
5 Critical Strategies for Identity Threat Protection & Exposure Resilience in 2025
Defending against the rising tide of identity threats requires an overall shift in our current approaches. The account-centric model of current business security postures is no longer sufficient in this fight. There are far too many hidden exposure risks that can impact an organization’s overall defenses.
Holistic identity threat protection – including continuous monitoring for hidden identity exposures, rapid response to exposed identity data, and automated remediation, are the keys to outpacing adversaries before they strike.
Ultimately holistic identity threat protection isn’t just about deterring threats, and it isn’t just about making it more expensive for criminals to come after your business. It is about stopping attacks by making stolen data useless.
Strengthen Access Controls with Zero Trust
To reach a sufficient Zero Trust implementation, it’s critical to continuously evaluate each user and device. This includes taking into account how your employee identities, devices, and access are perceived by criminals on the darknet. Continuously check for employee identity exposures to inform your policy engine when an identity is compromised.
Enhance Third-Party Security
Assess and mitigate exposure risks associated with third-party applications, vendors, and supply chain partners upfront when establishing new relationships and on a continuous basis to prevent weak links in your security.
Mitigate the Risk of Stolen Cookies
Even with MFA in place, cybercriminals can bypass authentication and hijack an active web session. Monitor for compromised cookies as they appear on the darknet and invalidate sessions to prevent unauthorized access to critical workforce services and to safeguard consumer sessions from fraud.
Improve Password Hygiene and MFA Resilience
Promote the use of password managers, enforce strong password policies, including banning weak passwords and automatically resetting newly exposed passwords, and implement MFA.
Continuously Monitor for Holistic Identity Exposures
Leverage advanced identity analytics that detect and correlate employee and customer data exposed in breaches, exfiltrated by malware, or phished by bad actors.
Defending the New Frontier
“That’s our new frontier out there, and it’s everybody’s business to know about [identity threat protection].”
Modern identity threats pose risks that extend not just to individuals but to organizations and global economies. A layered security approach is essential. Security teams have long invested in solutions like IAM and beyond to protect accounts, but these defenses still leave gaps in the face of modern cybercrime.
Cybercriminals are working tirelessly to aggregate stolen credentials, PII, and other identity data from breaches, malware infections, phishing kits, and underground markets – all of which fuel account takeover, fraud, and ransomware attacks. Understanding how cybercriminals exploit identity data is key to staying ahead, not just reacting after an attack.
SpyCloud’s approach extends beyond traditional identity security, providing visibility into the darkest corners of the criminal underground where stolen credentials, personal information, and financial data are actively traded. SpyCloud delivers curated identity analytics and automated remediation to help organizations counter these evolving threats.
By mapping the web of stolen data to holistic identity profiles, businesses can proactively mitigate risk before criminals weaponize what they have in hand. As identity-based cybercrime continues to grow, security teams must move beyond traditional perimeter defenses and adopt a more proactive, holistic approach to identity threat protection.

SPYCLOUD HAS PIONEERED A HOLISTIC APPROACH
to proactively prevent identity-based threats, setting a new standard for security and fraud prevention teams charged with defeating cybercrime. Learn how we can copilot the journey with you.
ABOUT SPYCLOUD
SpyCloud transforms recaptured darknet data to disrupt cybercrime. Its automated holistic identity threat protection solutions leverage advanced analytics to proactively prevent ransomware and account takeover, safeguard employee and consumer accounts, and accelerate cybercrime investigations. SpyCloud’s data from breaches, malware-infected devices, and successful phishes also powers many popular dark web monitoring and identity theft protection offerings. Customers include seven of the Fortune 10, along with hundreds of global enterprises, mid-sized companies, and government agencies worldwide. Headquartered in Austin, TX, SpyCloud is home to more than 200 cybersecurity experts whose mission is to protect businesses and consumers from the stolen identity data criminals are using to target them now.