The criminal underground is a full-fledged industry, fueled by the weaponization of billions of identity exposures in circulation on the darknet – everything from stolen credentials and PII, to credit card data and session cookies that fuel targeted, identity-based attacks.
Armed with AI, automation, and commoditized attack services, bad actors are systematically dismantling the security infrastructures you’ve invested years building.
When you’re in the thick of it, it can be hard to tell what’s working and what isn’t, as well as where to double-down.
That’s why we do an annual survey of security leaders and practitioners – and summarize the findings in our Identity Threat Report – to create helpful benchmarks and gut-check the state of defenses in the face of mounting identity-based attacks like account takeover, session hijacking, ransomware, and fraud.
Findings from the 2025 Identity Threat Report
The 2025 SpyCloud Identity Threat Report examines the true scope of identity-based risks, based on a survey of more than 500 security professionals, and shows that for many, yesterday’s playbook is outdated. Today’s adversaries are already making their way inside networks – masquerading with legitimate identities that slip past perimeter defenses you’ve invested years building.
The findings also reveal a dangerous paradox at the heart of modern cyberdefense: 86% of leaders express confidence in their defenses, yet 85% of organizations report being affected by ransomware in the past year – even more alarming, nearly 31% experienced between 6 and 10 incidents.
The gaps extend beyond ransomware. Nearly half of corporate users have been infected by malware sometime in their digital history. More than two-thirds of respondents report being significantly or extremely concerned about broader identity-based cyberattacks, including phishing and nation-state threats.
Leaders rate their detection and response capabilities highly; however, as the data highlights, most lack the necessary visibility, investigation, and remediation workflows to respond effectively.
We’ve outlined the key findings from this year’s survey and what respondents are (or aren’t) doing to mitigate the ever-changing identity threat landscape.
And one truth is very clear: confidence does not equal protection.
The leadership blind spot: When confidence meets reality
The survey responses in this year’s report underscore the divide between perceived readiness and actual outcomes.
While 86% of leaders feel confident in stopping identity-based attacks, the data tell another story.
- Only 41% reset credentials after phishing
- Just 54% reset passwords after malware infections
- A mere 38% can detect historical identity exposures that create ongoing risk
- Fewer than 20% have automated identity exposure remediation capabilities
Ransomware is ubiquitous
Ransomware remains one of the most impactful identity-based threats, but there appears to be a noteworthy confidence divide among teams when it comes to how prepared teams feel to defend against the threat.
Nearly half of CIOs and CISOs (45%) say they are “very confident” in their ransomware defenses, compared to just 28% of team leads and security directors. Executives often focus on metrics and big picture milestones, while those on the front lines grapple with constant alerts, time-consuming manual investigations, and remediation steps that rarely close the full threat loop.
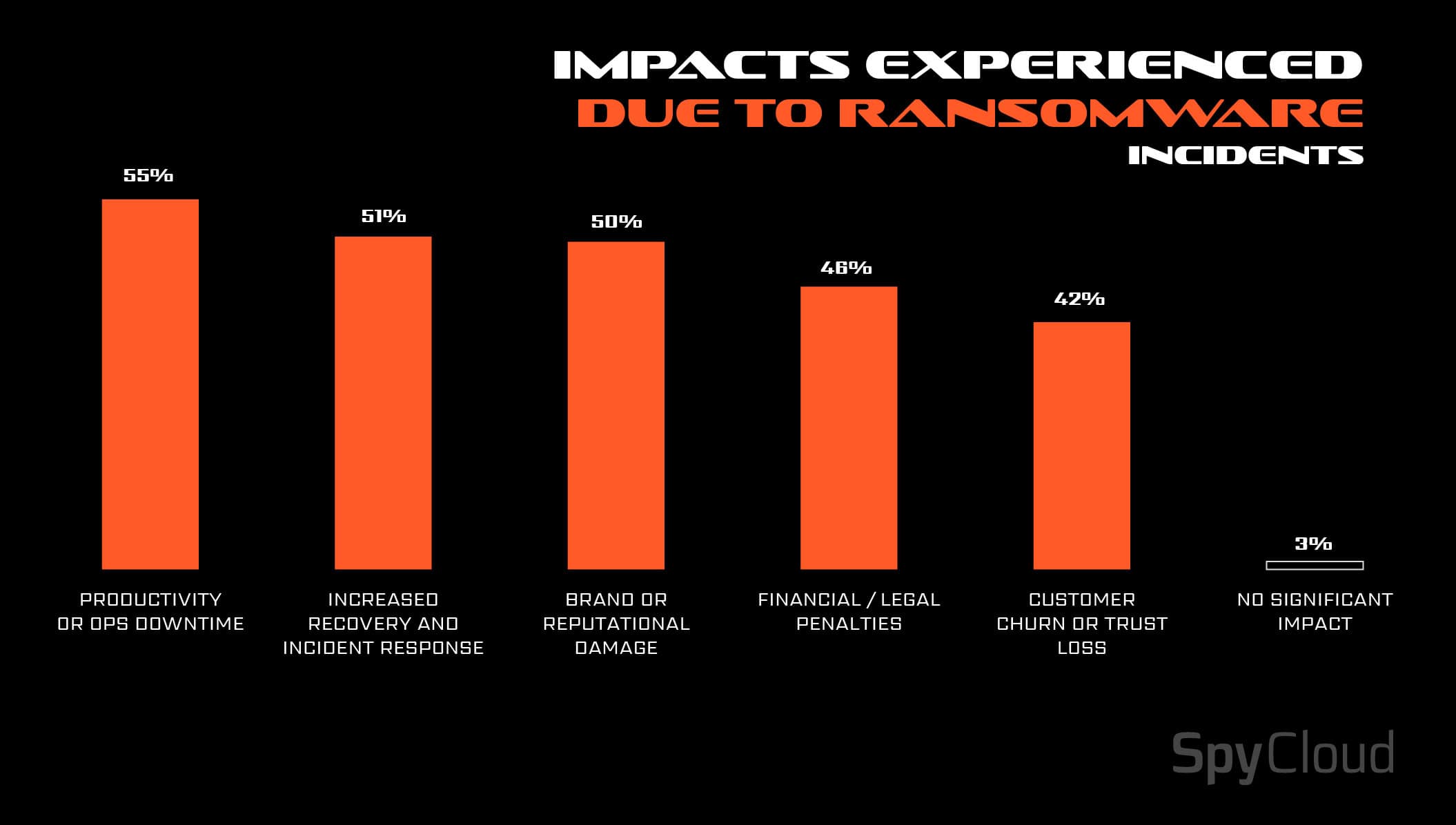
According to the report, the impacts are quite real:
- 85% of organizations were impacted by ransomware in the past 12 months
- 56% incurred cumulative costs exceeding $1 million per incident
- 50% reported reputational damage, while 55% experienced operational downtime
Phishing: The primary attack vector for ransomware
Phishing remains the dominant threat, with 40% of organizations ranking it as their top concern. It is also the top initial access vector for ransomware attacks in 2025, responsible for 35% of cases, up from 25% in 2024.
Of note from previous SpyCloud research, we’ve seen the the Black Basta ransomware group illustrate the clear connection between phishing and ransomware. Leaked internal chats reveal how the group leaned into phishing to gain initial access for subsequent ransomware attacks, leveraging spoofed login pages for Microsoft Teams, Fortinet VPN, Citrix, and Office 365.
Unfortunately, attackers continue to modernize and scale their phishing efforts through techniques including:
- AI-generated lures
- Phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) offerings such as Evilginx, Tycoon 2FA, and FlowerStorm
- Adversary-in-the-middle (AiTM) frameworks that intercept valid multi-factor authentication tokens
Infostealer malware silently fuels compromise
If phishing is loud and visible, infostealer malware is stealthy yet prevalent. SpyCloud analysis shows that approximately 1 in 2 corporate users have been infected by an infostealer at some point in their digital history, whether that be on a managed or unmanaged device.
Additionally, 66% of infections occur on devices already running endpoint security solutions or antivirus programs. Even with coordinated takedowns, which affected stealers like LummaC2 this year, there doesn’t seem to be an end in sight to the malware threat.
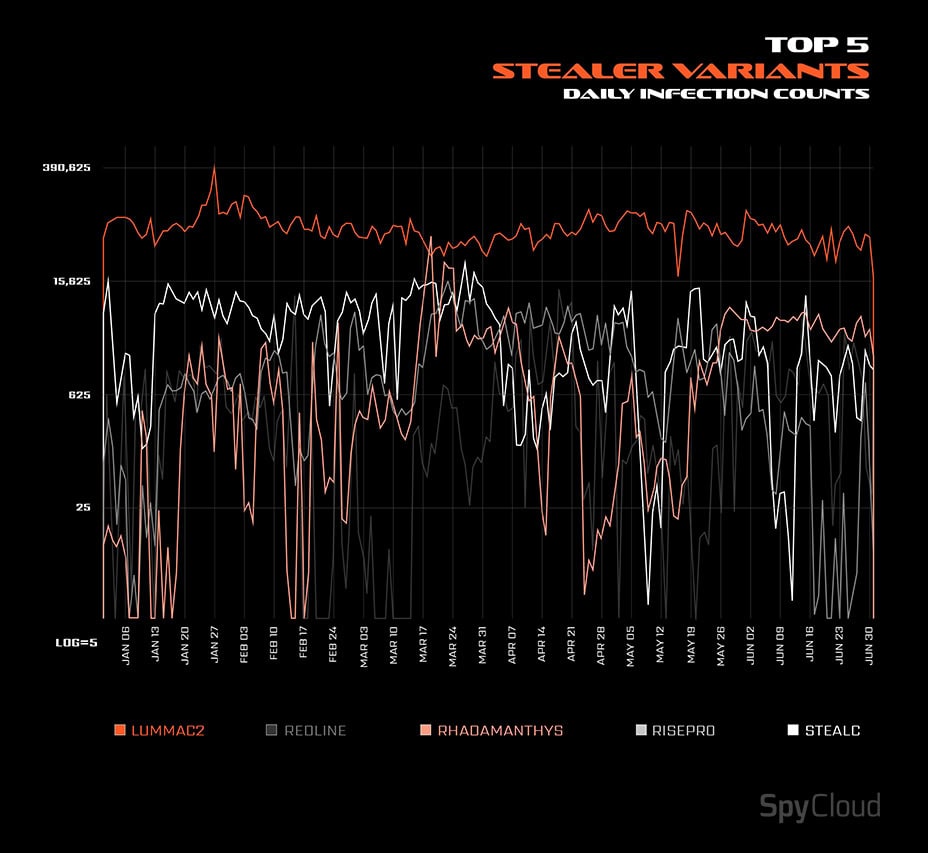
LummaC2 has dominated since late 2024, but while Windows is overwhelmingly the target of commodity malware, devices running macOS have also seen notable increases in targeting this year as well, largely thanks to highly-available macOS stealers like Atomic Stealer.
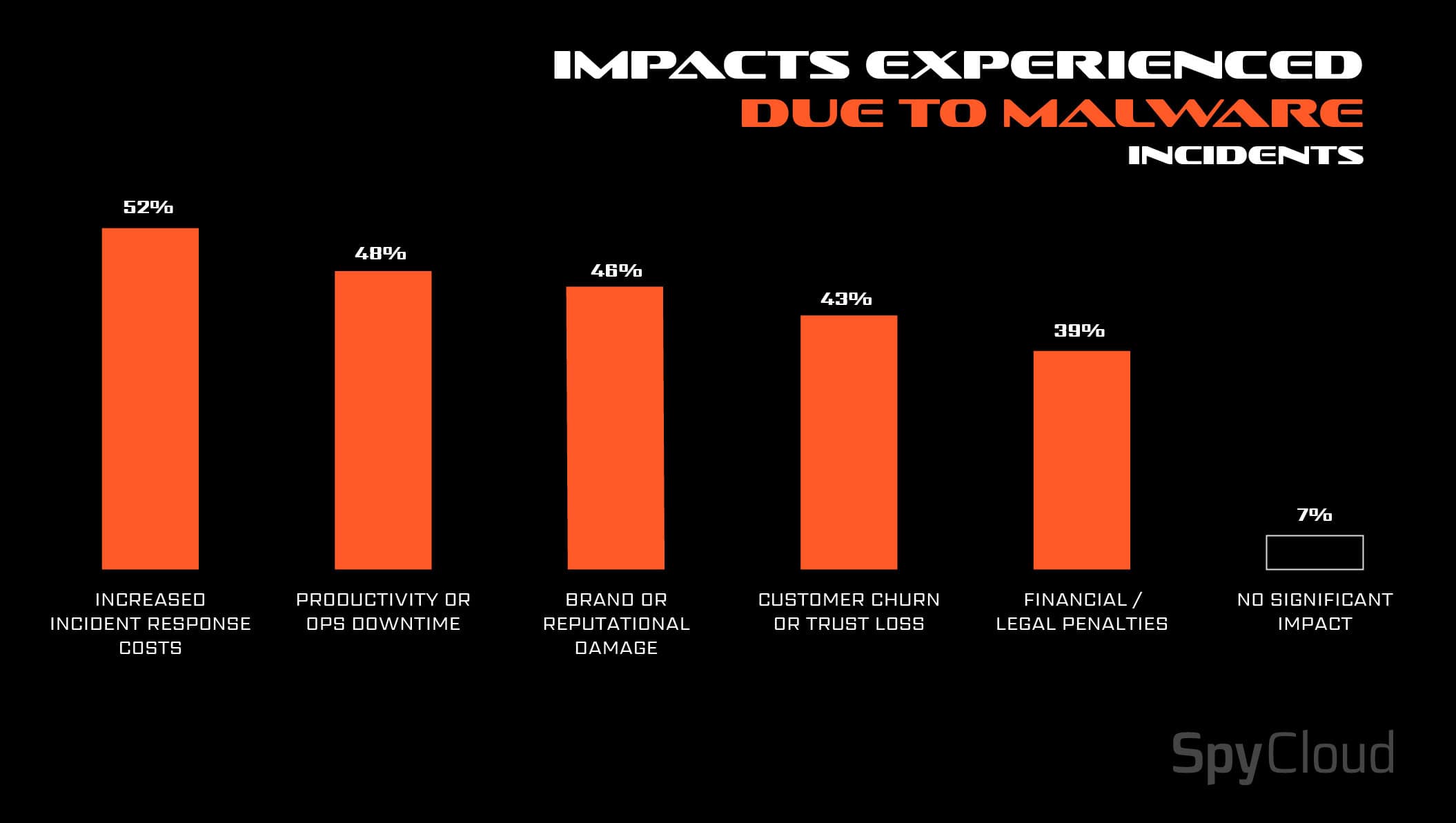
What has malware siphoned from your users?
The rising cost of ransomware and malware
The financial and operational toll of identity-driven attacks is significant. This year’s report shows the broad range of implications, ranging from operational downtime to increased response costs and reputational damage:
- 97% of respondents affected by ransomware incidents reported significant business impact
- 93% of malware victims reported significant business impact
The supply chain expands the identity attack surface
Identity-related incidents have surged, and the new report shows that identity sprawl is moving well beyond traditional perimeters, and even organizations that believe they are doing a good job struggle to contain it.
This challenge is especially visible in supply chain risk, where interconnected vendor ecosystems have become an attractive entry point for attackers. Certain sectors are especially vulnerable:
- IT vendors face 6x higher exposure risk
- Telecom industry: 5x elevated threat levels
- Software companies: 4x increased vulnerability
- Manufacturing and retail: 3x baseline risk
AI tilts the balance of power
92% of organizations agree that AI-powered cybercrime has intensified risk, yet only 47% currently use AI tools in their security operations. This creates a potentially dangerous asymmetry where criminals leverage AI to scale precision attacks while defenders remain hampered by manual processes.
Attackers use AI to do things like:
- Craft personalized phishing lures
- Spin up phishing pages in seconds
- Write malware that evades detection
- Generate deepfake-enabled social engineering
One example is the Darcula phishing kit, which allows even novice actors to replicate trusted brand sites instantly.
While AI is certainly not a silver bullet for defenders, when paired with contextual data, it can enhance detection for more accurate and automated remediation and fight fire with fire. Survey respondents who do use AI reported faster investigations, shorter dwell times, and stronger remediation.
AI Is fueling cybercrime and defense
92% say AI has intensified risk, but only 47% use AI defensively. SpyCloud AI-powered solutions pair AI with enriched data to help you close that gap.
Charting a course correction
The path forward requires organizations to shift from perception to action – and to adopt an identity-first mindset that treats exposed data as the primary threat surface. To keep pace, defenders should focus on these core areas:
- Return to fundamentals: Continuously monitor for identity exposures across employees, consumers, and third parties.
- Automate remediation: Automate credential resets and session invalidation as part of standard remediation.
- Unify teams: Only 42% strongly agree that identity protection roles are clearly defined. Alignment across IT, IAM, and security leadership is essential.
- Meet or beat bad actors’ speed: Leverage trusted data and AI to accelerate investigation and incident response
Get ahead of identity-driven threats
The identity attack surface is vast, and identity exposures are not one-time events. Once stolen, data is often repackaged, resold, and reused indefinitely unless remediated. Criminals have billions of data points and increasingly efficient tools at their disposal to disrupt organizations of all sizes.
SpyCloud’s collection of recaptured identity assets has ballooned to 63.8 billion identity records, a 24% increase year-over-year, adding to a pool of more than 850 billion exposed assets circulating on the darknet.
The 2025 SpyCloud Identity Threat Report makes one thing clear: confidence without adequate defensive action is a dangerous illusion.
To outpace identity-driven threats, defenders should look to continuous identity monitoring with a holistic lens – accounting for past and present, as well as corporate and personal exposures – automated remediation, and unified workflows across teams. Organizations that act now will be able to better protect their people, data, and operations. Those who do not risk remaining trapped in unending cycles of compromise and recovery.
Download the full 2025 SpyCloud Identity Threat Report to explore detailed insights, threat trends, and benchmark data.
Key takeaways from the 2025 Identity Threat Report
- Confidence ≠ protection: 86% of organizations feel confident in their defenses – yet 85% were affected by a ransomware incident in the past year.
- Infostealers are a silent epidemic: Despite the pervasiveness of infections, defenders only reset user passwords after exposure 54% of the time.
- Phishing remains dominant: Ranked the top threat by 40% of organizations, phishing continues to be the leading entry point for ransomware attacks.
- AI is reshaping cybercrime: 92% believe AI is increasing threat complexity, with phishing-as-a-service and deepfakes accelerating identity-based attacks.
- Supply chains and unmanaged devices are major blind spots: Security teams report limited visibility into exposures beyond their direct control, while supply chain risk multiplies.
Download the full 2025 SpyCloud Identity Threat Report for detailed insights, threat trends, and benchmark data.
FAQs
The confidence gap stems from a fundamental disconnect between executive perception and operational reality. This disparity occurs because executives often rely on compliance dashboards, audit results, and high-level security metrics that can obscure deeper operational risks or issues. Meanwhile, practitioners deal with the daily reality of alert fatigue, manual remediation processes, and incomplete workflows that sometimes leave critical gaps unaddressed.
When it comes to the threats that survey respondents are most worried about leading to follow-on attacks, this year’s survey shows phishing as the top concern, followed by supply chain exposures, malware infections, and insider threats.
Identity exposure creates multiple pathways for ransomware deployment by providing attackers with the legitimate access they need to move undetected through corporate environments. This often takes shape with initial compromise, followed by legitimate access, lateral movement, environment preparation, and then ransomware deployment.
AI is fundamentally reshaping identity-based attacks by democratizing sophisticated cybercrime capabilities and accelerating attack timelines. Our research shows that 92% of organizations recognize AI-powered cybercrime as an intensified risk, yet only 47% are using AI tools defensively – creating a dangerous asymmetry.
SpyCloud analysis shows the following industries face the highest identity threat risk: IT vendors (6x baseline risk); Telecommunications (5x risk); Software companies (4x risk); Manufacturing and Retail (3x risk each); Healthcare (2x risk); Energy and Utilities (2x risk)