USE CASE: RANSOMWARE PREVENTION
Disrupt the Ransomware Attack Chain
with Identity Threat Protection
Ransomware doesn’t begin with file encryption – it begins with compromised identities. SpyCloud stops ransomware before it starts by detecting and remediating exposed credentials, session cookies, and personal data that adversaries use to gain a foothold.
Whether the exposure results from malware, phishing, or a third-party breach, reclaiming control over exposed data means you can cut off initial access, stop lateral movement, and prevent escalation – keeping your organization one step ahead.
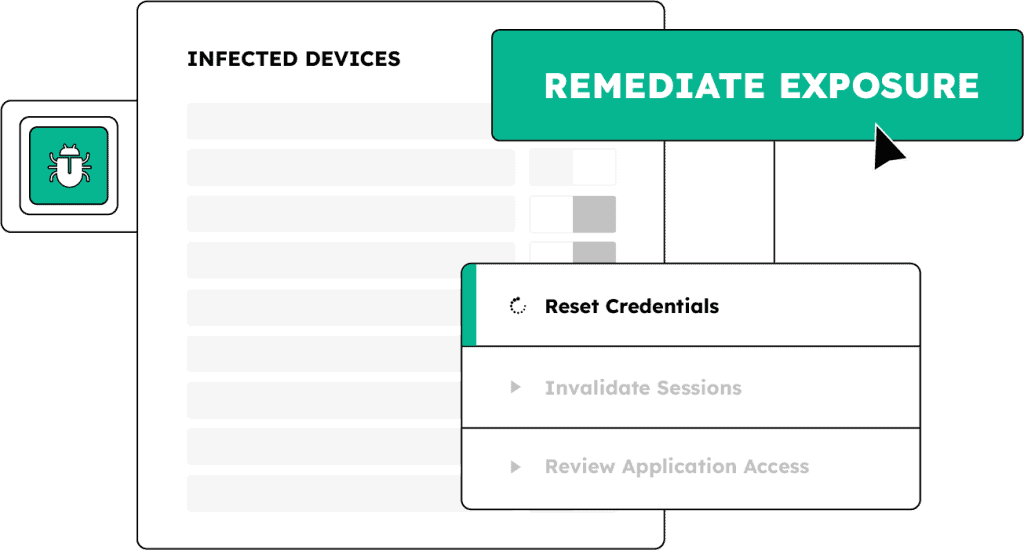
Take down ransomware risk at the root
The key to preventing ransomware is to detect and remediate loss of access.
Ransomware attacks often stem from phishing attacks or infostealer infections. Security professionals report that phishing is the most common entry point in ransomware attacks, and recent research found that one-third of ransomware events were preceded by a stealer infection in the previous 16 weeks.
By remediating exposed access early, you can prevent phishing and malware from escalating into a full-blown ransomware attack.
Uncover user identities targeted by phishing and infostealer malware
Stop attackers from using stolen authentication data to move laterally or escalate privileges
Integrate actionable identity insights into your workflows to shrink dwell time and minimize ransomware risk
EXPLORE PRODUCTS
SpyCloud’s identity intelligence is your ransomware early warning signal. Cut off initial access by remediating exposed identity data and malware-compromised apps.
Neutralize malware threats before they escalate into costly ransomware incidents
Stop cybercriminals from using stolen credentials to take over accounts and escalate ransomware campaigns
Protect session cookies that attackers use to bypass MFA and gain initial access
Whenever we get an alert from [SpyCloud] we always follow it up as it is always fresh intel. Using SpyCloud helps us break into the cycle of identity access brokers and remediate compromised accounts before they are used against us.
EXPLORE WHO USES SPYCLOUD
Defenders
we help
Integrations





