IBM’s latest Cost of a Data Breach Report is here – and the numbers in this year’s report reveal a paradox: while average global breach costs dropped slightly to $4.44 million, the United States hit a record-breaking $10.22 million per breach.
For security professionals focused on identity threat protection, the findings underscore how compromised identities remain at the heart of today’s most damaging cyberattacks.
What’s inside IBM's Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025
The 2025 report offers a clear view into how identity-based threats are shaping breach outcomes. Credential-related attacks, supply chain compromise, and malicious insiders continue to drive up costs, particularly in the U.S., where the average breach hit an all-time high.
It also highlights a growing gap between organizations using AI and automation to detect and respond to threats and those relying on manual processes. That difference now amounts to millions in cost savings.
Identity risks and trends from the 2025 report
Initial access vectors: Phishing and credential exposure are top threats
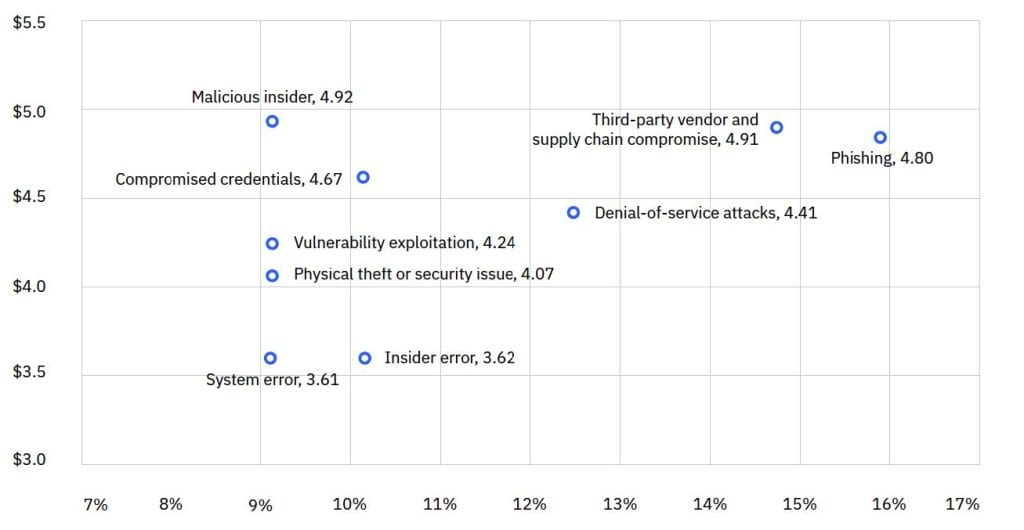
IBM found that phishing (16%) has overtaken compromised credentials this year as the top initial access vector, but both remain top drivers of identity-based attacks.
With AI-generated phishing emails now taking minutes instead of hours to create, it’s no surprise phishing climbed to the top spot. Attackers are leveraging generative AI to scale deception, and security teams must evolve accordingly.
The true cost of compromised identities
Measured in USD millions; percentage of all breaches. Source: 2025 IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report, Page 17, Figure 9.
While phishing grabs headlines, breaches where compromised credentials were the initial access vector still pack a devastating punch at $4.67 million per breach. These incidents represent the downstream impact of successful credential harvesting – whether through phishing, malware infections, or third-party data breaches. The 246-day average time to identify and contain these attacks highlights a critical challenge: organizations often don’t know their employees’ credentials are circulating in the criminal underground until it’s too late.
The report also reveals that malicious insider attacks carry the highest average cost at $4.92 million for an impacted organization, often because these incidents are harder to detect and resolve due to their trust-based nature.
While less frequent than external attacks, malicious insiders remain high-impact. Their activities often extend dwell time and increase remediation costs due to complex investigations, forensic requirements, and regulatory fallout. IBM flags insider threat readiness, including monitoring, access controls, and Zero Trust enforcement, as cost-mitigating levers.
Supply chain compromise creates cascading risks
Third-party vendor and supply chain compromises emerged as both the second most frequent attack vector (15%) and second costliest ($4.91 million). These attacks took the longest to detect and contain at nearly 9 months (267 days), reflecting the complex web of relationships that attackers exploit.
From an identity threat perspective, supply chain attacks often succeed because of weak exposure management across vendor relationships. When a supplier’s credentials are compromised, attackers can pivot into customer environments using legitimate access pathways. This cascading effect explains why these incidents are so costly and time-consuming to resolve.
AI-driven attacks: Escalating and under-governed
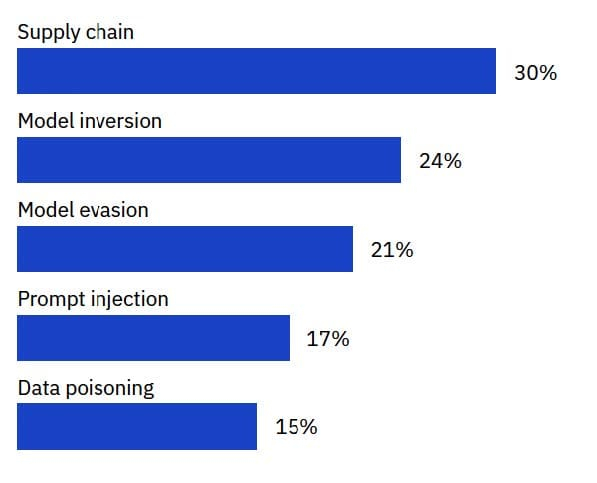
AI is now fueling the attacker’s playbook – and bad actors largely took advantage of the supply chain here, too. Supply chain compromise made up a hefty 30% of incidents involving AI models and apps.
From organizations that reported a security incident involving an AI model or application. Source: 2025 IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report, Page 28, Figure 19.
Among organizations that experienced AI-related breaches, 97% lacked proper AI access controls. Additionally, 20% of organizations suffered breaches involving shadow AI, adding an average of $670,000 to breach costs.
This represents a new frontier for identity-based threats. Shadow AI creates unmonitored pathways for credential exposure, while poorly secured AI systems become high-value targets for attackers seeking to compromise both data and AI models themselves.
Ransomware resistance grows, but costs remain high
The report shows encouraging signs of ransomware resistance, with 63% of organizations refusing to pay ransoms (up from 59% in 2024). That being said, the average cost of ransomware incidents remains substantial, particularly when disclosed by attackers ($5.08 million).
This trend reflects a mature understanding that paying ransoms doesn’t guarantee recovery and often funds future attacks. For identity threat protection, it underscores the importance of preventing initial access rather than trying to negotiate after compromise.
AI and automation: Still the most effective defense
Organizations using AI and automation extensively achieved notably better results than their peers according to the report: 80 days faster breach identification and containment, and $1.9M lower breach costs.
However, adoption remains uneven, with only 32% of organizations using AI and automation technologies extensively. For identity-focused security programs, automation is essential for analyzing the vast amounts of data from the criminal underground and correlating it with internal identity exposures.
Final thoughts: Identity is the attack surface
If you have the time, we always recommend giving the full report a read.
As IBM reaffirms, identity compromise remains the most persistent – and costly – attack vector. Even as breach costs drop globally, the U.S. average climbs, and dwell times only shrink for mature, automated security environments.
SpyCloud’s mission – to disrupt cybercrime by preventing identity-based threats like account takeover, fraud, and ransomware – has never been more aligned with today’s threat landscape. Organizations that monitor for compromised identity data and automate remediation are best positioned to mitigate breach impact.
The report’s findings reinforce several key principles for protecting against identity-based threats:
Speed matters
The global average breach lifecycle dropped to 241 days, but faster detection and containment directly correlate with lower costs. Organizations need real-time visibility into identity exposures from the criminal underground.
Prevention beats response
While incident response capabilities are crucial, preventing compromise through proactive monitoring of exposed data sources provides the greatest cost savings.
Comprehensive coverage is essential
With attack vectors spanning traditional credential compromise, phishing, supply chain attacks, insider threats, and more, organizations need to address all potential entry points.
Investment in automation pays dividends
The clear cost benefits of AI and automation in security operations make a compelling case for expanding these capabilities in workflows across teams and functions.
Organizations that invest in comprehensive identity threat protection – combining real-time monitoring of criminal data sources with automated remediation capabilities – are best positioned to prevent the million-dollar breaches that dominated this year’s findings.
The question isn’t whether your organization’s identity data is circulating in the criminal underground, it’s whether you have the visibility and tools to act on that exposure before attackers do.
You're one step away from checking your exposure against billions of darknet assets.